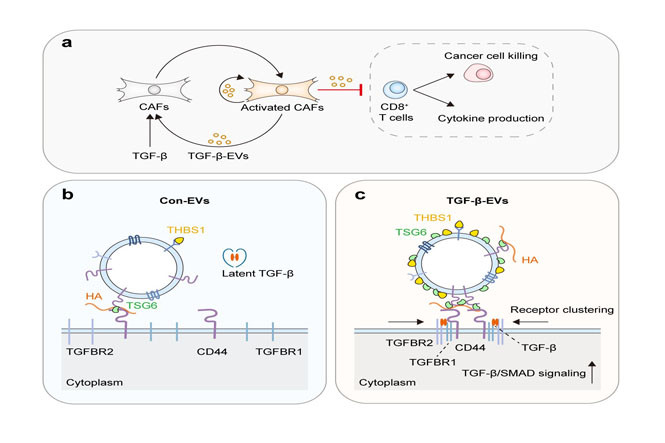
Extracellular vesicle coronal proteins enhance TGF-β signaling in target cells by inducing receptor clustering
We set out to investigate how extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from TGF‐β‐activated cancer-associated fibroblast (CAFs) (TGF‐β‐EVs) sustain CAF activation and impair the cancer cell-killing ability of CD8+ T cells. Rather than the transfer of EC cargo to recipient cells, we discovered that an EV-target cell contact-dependent process is the key determinant. TGF‐β‐EV surface-associated (coronal) proteins promote the proximity of multiple receptors in target cells, enabling potent TGF-β receptor signaling.
C. Li, A. Enciso‐Martinez, et al. “Surface‐Associated Proteins on Extracellular Vesicles Remodel the Tumor Microenvironment by Potentiating TGF‐β Signaling in a Contact‐Dependent Manner.” Adv. Sci. (2025): e13286.